Stainless steel can be found everywhere in our daily life, from small surgical instruments and cutlery and cookware, to large construction materials and industrial equipment. Laser cutting is favored by more and more stainless steel processors because of its high speed and high accuracy.
This article will cover the basics of stainless steel laser cutting, cutting difficulties and costs.
What is Stainless Steel Laser Cutting?
Stainless steel laser cutting is a process in which a very high power density laser beam is focused onto the surface of stainless steel, causing a rapid increase in the local surface temperature and rapid melting, vaporization and ablation.
At the same time, through the beam coaxial high-speed airflow will be stainless steel melt blowing away, to realize the workpiece precision cutting.
Why Is Stainless Steel Difficult to Cut?
The main reason why stainless steel is difficult to cut is inseparably related to its unique physical and chemical properties, especially in the traditional processing methods will face the following challenges:
High reflectivity
Stainless steel, especially austenitic 304, 316 on the fiber laser reflectivity up to 70%, much higher than carbon steel. This makes it difficult to couple the laser energy efficiently, and higher power is required to initiate a cut compared to cutting carbon steel of the same thickness.
High melt viscosity, easy to hang slag
As stainless steel contains elements such as chromium and nickel, it has high melt viscosity and poor fluidity. This means that the auxiliary gas is difficult to completely blow off the slag, the lower end of the cut is easy to form a “tear drop” slag.

Thick plate cutting energy attenuation
When cutting stainless steel plate thickness > 10mm, the laser is reflected many times in the kerf, resulting in uneven energy distribution, which leads to increased kerf taper and slag accumulation at the bottom.
Chop offset
Under the high temperature of the laser, zinc, manganese and other low-boiling point elements in stainless steel are preferentially evaporated, and the evaporation of these elements leads to a shift in the composition of the edge of the kerf, and the corrosion resistance of the edge of the cut may be reduced.
What’s the Best Tool for Cutting Stainless Steel?
There are many ways to cut stainless steel, such as laser cutting, CO2 cutting, CNC milling machine, water cutting, plasma cutting and so on. Why is laser cutting the best tool?
High cutting precision
The laser focusing spot formed by focusing mirror is as small as 0.01mm, which can instantly heat the stainless steel to the melting point or vaporization temperature, with the high-pressure gas to blow away the molten material, forming a very narrow to 0.1mm slit, the cut surface is smooth and burr-free, and the heat-affected zone is extremely small.
Excellent cutting quality and not easy to deform
laser high temperature vaporization of the material in a very short period of time, the kerf perpendicularity is good, the surface roughness can be up to Ra6.3μm or less, reducing the secondary processing. Plus laser stainless steel cutting heat concentration, resulting in very low thermal deformation, which is particularly evident in the cutting of thin stainless steel plate.

High material utilization
Compared to traditional cutting processes, such as flame cutting, laser cut stainless steel has a slit that is more than 50% narrower, and with nested nesting you can save up to 30% of material.
Long-term cost advantage
Ss laser cutting’s equipment initial investment is high, but the comprehensive use of energy consumption and consumables, compared with plasma cutting machine, cnc milling machine, carbon dioxide cutting, etc., the cost of processing a single piece is only 1/3-1/2 of the cost of the other cuts.
Common Problems of Laser Cutting Stainless Steel
Are you experiencing some difficulties when laser cutting stainless steel? This section collates common phenomena in cutting stainless steel, and proposes solutions after analyzing them.
Burr Defects
In piercing of stainless steel, the laser beam hits the surface of the stainless steel and starts to melt. The melt is ejected onto the surface of the material. It splashes around the small holes and forms whisker burrs. These whisker burrs cause scratches on the cut surface and also affect the profiling action of the electrostatic capacity sensor.

[Reason] When oxygen is used as an auxiliary gas, the molten metal oxidizes during the piercing process and does not form whiskers and does not adhere well to the surface of the stainless steel material.
But when nitrogen is used as an auxiliary gas, the molten metal will not be maintained ah, the viscosity of the melt is low, it will stretch to become whiskers, coupled with the melt of the language of the surface of the material between the tightness of the strong, and then piled up in the small holes around.
How to solve stainless steel whisker burr?
[Solution] To solve the whisker burr of stainless steel laser cutting, it is necessary to prevent both splashing of molten metal and adhesion.
(1) Reduce the production of molten material
①We can adjust the perforation conditions, increasing the frequency to reduce the output power of a single pulse will be effective in reducing the amount of molten. However, it should be noted that when using this processing condition, the heat input will be increased and thus cannot be used for thick plate cutting.
② Utilize an auxiliary gas or measured blowing gas to blow away the molten metal ejected from the perforation hole. The results of processing with auxiliary gases at 0.05 MPa and 0.7 MPa pressure are shown in the figure. As can be seen, the amount of molten slag adhering to the surface is less when high pressure gas is used.

(2) Preventing adhesion
Applying a barrier film to the stainless steel surface of the material prevents the molten metal from adhering. This is because during perforation, the resulting molten metal accumulates on the barrier film rather than adhering directly to the stainless steel surface.
For the selection of the isolation film, a slag preventive agent or a surfactant that facilitates subsequent processing can be used.
(3) Burr Removal
What can be done to remove the burrs that have been created? We can cut very small round holes in the vicinity of the perforated holes and remove the molten metal along with the holes when cutting them. Or move the focal point position upward after piercing the hole to melt the buildup for a second time and use gas to blow it away.
Processing 1mm Stainless Steel Sheet Produces Deformation
When laser cutting stainless steel in the shape of a thin strip, there is a discrepancy in the width of the short axis at the ends and in the center.
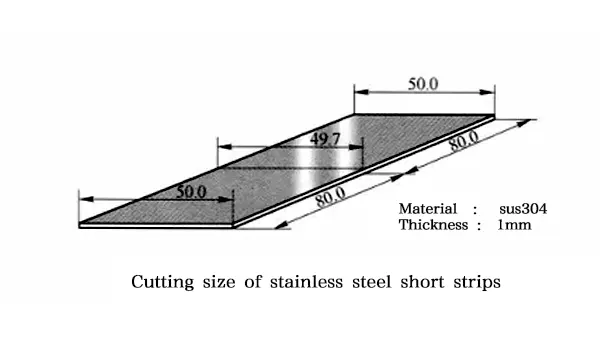
[Reason] The main reason for the difference in the width of the short axis is that the heat of the molten metal in the part of the kerf raises the temperature of the processed object, and the cutting will be carried out in the high temperature state of the material. When the temperature decreases after cutting, shrinkage of the machined shape leads to the error described above. In addition, the shape of the workpiece is shifted within the kerf width of about 0.5mm, which is also the cause of the error in the cut size.
[Solution] If the processed shape is shifted within the kerf, the problem can be solved by installing a micro-connection between the processed shape and the material outside the processed shape. The method of setting the micro-connection is to pause in the middle of cutting and then move the machining trajectory slightly before continuing cutting. Setting up the micro-connection is mandatory to maintain the distance between the processed shape and the material outside the processed shape, which prevents deformation.
In the processing of hot rolled carbon steel materials, the phenomenon of different amounts of deformation at different processing positions occasionally occurs. This may be due to the steel in the cooling after rolling, the material ends are not sufficiently cooled, the residual stress is relatively high, the stress is released in the laser cutting, resulting in deformation.
Direct Cutting of Film-Laminated Stainless Steel
Many stainless steels on the market for sale will have a protective film applied to the surface to prevent scratches. Generally speaking, the protective film will be removed before cutting, and then the film will be put back on after cutting.
However, more customers require ss laser cutting with the film applied. the effect of film applied stainless steel in cutting is not stable, sometimes the effect is very good, sometimes the protective film peeling will happen.

[Reason] So why does it cause the protective film peeling? This is because in the cutting, did not enter the slit auxiliary gas will diffuse to the surface of the stainless steel, invasion of the protective film and the surface of the material within the gap, so that the protective film peeling.
[Solution] When cutting the protective film, the intensity of the laser beam pattern at the cutting edge should be sharply distributed, and care should be taken not to allow the laser to become turbulent. The speed condition should be set to high speed condition to reduce the thermal influence of the laser on the protective film.
Stainless Steel Laser Cutting Cost
Stainless steel laser cutting cost is an important factor affecting the choice of laser cutting machine. Let’s analyze the cost of investing in laser cutting stainless steel one by one.
Initial Investment Cost
Stainless steel laser cutting machine price is the initial investment cost of ss laser cutting, and it is also a fixed cost, and its specific price depends on the equipment supplier, power, processing width, and additional features (such as the exchange table, loading and unloading system, and dust removal system), and so on. In general, the higher the power, the higher the cutting capacity, but the higher the initial investment cost will be.
Running Costs
Running costs are also variable costs, i.e. the cost of using the equipment, including power consumption, gas consumption, maintenance costs and labor costs.
Power consumption
Stainless steel fiber laser cutting machine photoelectric conversion efficiency of about 30% -40%, that is, 1kW laser actual power consumption of about 2.5-3.3kW. The specific cost of electricity depends on the location of the power tariffs.

Gas consumption
The gas consumed in the cutting process to prevent oxidation and blow away the molten material is also one of the running costs. For example, nitrogen, oxygen, argon, etc. The specific choice of which auxiliary gas depends on the t
ype of metal material to be cut. Many people will use compressed air in order to save cost when cutting, but the cutting quality is poor, easy to hang slag.
Maintenance cost
Stainless steel fiber laser cutting machine’s maintenance cost is mainly the replacement of optics, nozzles and the maintenance cost of the laser. Compared with CO2 laser cutting machine, the maintenance cost of fiber laser cutting machine is much lower, mainly because of the lower cost of consumables and the longer service life of the laser.
FAQs
The thickness of stainless steel that can be laser cut depends on the power of the equipment. 1500W-3000W lasers can cut stainless steel up to 8mm thick. 6kW-12kW lasers can cut stainless steel sheet up to 1-25mm thick. 15kW or more lasers can cut stainless steel sheet up to 30-40mm thick. Ultra high power laser cutting stainless steel sheet thickness up to 30-40mm.
Of course you can! Of course! 304 stainless steel can be laser cut effectively. This is due to the fact that 304 stainless steel has good thermal conductivity but lower reflectivity than aluminum, making it compatible with fiber lasers. Unlike ferritic or martensitic stainless steels, its austenitic structure minimizes the risk of cracking during the cutting process.
Laser cutting stainless steel is where the choice of auxiliary gas has a direct impact on cut quality, speed and cost.
If you pursue precision cutting without oxidized cuts, give preference to nitrogen, this is because nitrogen is an inert gas will not react with the substances in the stainless steel, the cut is silver-white original color, the cutting surface is smooth without hanging slag, without secondary treatment.
If you require high cutting speed and can accept the black oxide layer produced by oxidation of the cutting surface, then oxygen is a good auxiliary gas.
If you want to maximize cost savings and do not require high cutting results and speed, you can consider compressed air.
Conclusion
We have discussed the reasons why laser cutting stainless steel is difficult and analyzed in detail the common problems and solutions for cutting stainless steel and the cost of laser cutting stainless steel.
What are your other doubts about laser cutting stainless steel? You can tell us your doubts and thoughts.
If you are considering to choose stainless steel laser cutting machine with good quality, prompt after-sales service and cost-effective price, you can learn about the following XT LASER, which is one of the famous fiber laser equipment manufacturers in China. They will provide top-notch stainless steel cutting solutions according to your needs.

